Nidana Sthana: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
===Knowledge of disease=== | ===Knowledge of disease=== | ||
After thorough examination of an individual, one shall evaluate the disease. The second part of diagnostic protocol provides comprehensive knowledge of disease. This includes the methods to elucidate causative factors ([[hetu]]), observe premonitory signs and symptoms ([[purvarupa]]), clinical features[[rupa]], pathogenesis ([[samprapti]]), and pacifying factors ([[upashaya]]). The set of these five diagnostic tools is called as 'Nidana Panchaka'. This is described and applied in clinical practice to know each disequilibrium condition. | After thorough examination of an individual, one shall evaluate the disease. The second part of diagnostic protocol provides comprehensive knowledge of disease. This includes the methods to elucidate causative factors ([[hetu]]), observe premonitory signs and symptoms ([[purvarupa]]), clinical features ([[rupa]]), pathogenesis ([[samprapti]]), and pacifying factors ([[upashaya]]). The set of these five diagnostic tools is called as 'Nidana Panchaka'. This is described and applied in clinical practice to know each disequilibrium condition. | ||
The phenomena of a disease causing another disease is described as [[Nidanarthakara roga]]. [[Upadrava]] (complications), [[Udarka]] (marks of disease after it is cured) are applied for knowing the cause-effect relationship in pathogenesis of disease. | The phenomena of a disease causing another disease is described as [[Nidanarthakara roga]]. [[Upadrava]] (complications), [[Udarka]] (marks of disease after it is cured) are applied for knowing the cause-effect relationship in pathogenesis of disease. | ||
Revision as of 06:23, 10 July 2021
| Section/Chapter | Nidana Sthana Section 2/ Preamble |
|---|---|
| Preceding section | Sutra Sthana |
| Succeeding section | Vimana Sthana |
| Other Sections | Sharira Sthana, Indriya Sthana, Chikitsa Sthana, Kalpa Sthana, Siddhi Sthana |
| Author | Deole Y. S. |
| Reviewer | Basisht G. |
| Editor | Basisht G. |
| Year of publication | 2020 |
| DOI | 10.47468/CSNE.2020.e01.s02.001 |
| Total number of verses | 247 |
| Chapters | |
| 1. Jwara Nidana, 2.Raktapitta Nidana, 3. Gulma Nidana, 4. Prameha Nidana, 5. Kushtha Nidana, 6. Shosha Nidana, 7. Unmada Nidana, 8. Apasmara Nidana | |
Preamble of Nidana Sthana (Section on Diagnosis)
The section Nidana Sthana deals with principles of diagnosis of diseases. The term Nidana is applied for knowing the origin of disease (vyadhijanaka) and comprehensive information of disease (vyadhibodhaka). [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa.Nidana Sthana 1/1-2]
Fundamental principles of diagnosis
Important aspects of knowledge of disease
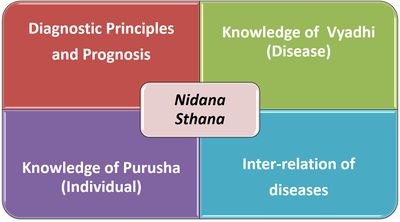
Nidana section studies diagnostic principles in view of two important aspects like knowledge of roga (disease) and rugna (patient). It always considers interaction between the individual and the affecting pathological entities. It also considers the prognosis and inter-relation of different diseases or co-morbid conditions.[Image 1: Aspects of Nidana Section]
Knowledge of the individual
Before knowing disease, one needs to know the self-healing capacity of the human being. This depends upon equilibrium of five components of health, namely dosha (regulatory functional factors of body and mind) , agni (digestive and metabolic capacity), dhatu (body tissues), mala (metabolic waste products) and psycho-spiritual state. Health is a state of equilibrium, whereas disease is a state of dis-equilibrium of any of these factors.
According to swabhavoparam vada, the resolution / destruction of the existing always happens naturally in the course of time. So the nature itself heals disequilibrium.[[Chikitsaprabhritiya Adhyaya#Swabhavoparama vada (theory of natural destruction)[Cha.Sa.Sutra Sthana.16/27].This aspect of host defense mechanism is important to be assessed for knowing natural healing capacity of an individual. In the fourth chapter,Prameha Nidana, the process of onset of disease through interaction between aggravating and pacifying factors is described [[Prameha Nidana#Process of Onset of Disease|[Cha.Sa. Nidana Sthana 4/4]. If the host defense factors are stronger than aggravating ones, then the disease will not occur and vice versa. Therefore, before making a diagnosis of a disease, examination of patient is important with emphasis on his prakriti (basic constitution), sara (quality of tissues) etc described in context of [[Rogabhishagjitiya Vimana#Examination of patient|ten fold examination of the patient[Cha.Sa.Vimana Sthana 8/94-131]. Every person has a unique constitution and hence the same biological investigations cannot be precise to assess his health status completely. Personalized assessment is important to diagnose normal and abnormal state of the individual.
Knowledge of disease
After thorough examination of an individual, one shall evaluate the disease. The second part of diagnostic protocol provides comprehensive knowledge of disease. This includes the methods to elucidate causative factors (hetu), observe premonitory signs and symptoms (purvarupa), clinical features (rupa), pathogenesis (samprapti), and pacifying factors (upashaya). The set of these five diagnostic tools is called as 'Nidana Panchaka'. This is described and applied in clinical practice to know each disequilibrium condition.
The phenomena of a disease causing another disease is described as Nidanarthakara roga. Upadrava (complications), Udarka (marks of disease after it is cured) are applied for knowing the cause-effect relationship in pathogenesis of disease.
Principles of management of disease are mentioned in brief in each chapter to denote pacifying factors of disease. Each chapter of this section follows the same protocol for comprehensive knowledge of disease.
Importance of eight chapters
This section comprises eight different chapters as described below:
- The first chapter, Jwara Nidana , introduces basic principles of diagnosis of a disease as well as the disease jwara with involvement of rasa dhatu as dushya.The chapter discuss diagnosis of disorders of hyper-pyrexia and various types of fever.
- The second chapter, Raktapitta Nidana, deals with various pathologies related to rakta dhatu.This chapter details the diagnosis of bleeding disorders.
- The third chapter, Gulma Nidana, deals with mamsa dhatu(muscle tissue) predominantly. This chapter describes diagnosis of lumps in abdomen, tumors.
- The fourth chapter, Prameha Nidana, involves meda dhatu (tissue fat) predominantly. This chapter describes the diagnosis of disorders of lipid metabolism, obstinate urinary disorders including diabetes.
- The fifth chapter, Kushtha Nidana, involves seven dushya (vitiated factors). This chapter deals with diagnosis of skin disorders.
- The sixth chapter, Shosha Nidana, deals with the pathology of emaciation. This chapter describes diagnosis of degenerative disorders that involve depletion of body tissues.
- The seventh chapter, Unmada Nidana explain insanity and psychotic disorders.
- The eighth chapter, Apasmara Nidana deals with epilepsy and seizure disorders.
These eight chapters represent pathogenesis of major diseases described in detail in this section. Each chapter directs towards variety of pathogenic processes related interaction of vitiated dosha with dhatu to cause disease.
Guidelines to diagnose anukta vyadhi (new or untold diseases in text)
There are innumerable diseases. Major diseases are mentioned in this text. Therefore one may not find complete description of certain diseases seen in contemporary era. Any new or unknown disease should be studied by assessment of vitiated dosha and dushya (vitiated factors). The criteria like type of pain, appearance (color), etiology, site, symptoms and name shall be applied for identification.(Cha.Su.18/42-43)
All endogenous diseases start with vitiation of dosha. The causative factors elucidated in the detailed history of a patient’s diet, lifestyle, psychological frame and others direct the vitiation of a specific dosha. Then their status (increase or decrease) can be assessed based on the premonitory signs and clinical features. Then after evaluation of aggravating (anupashaya) and pacifying (upashaya) factors is done, the sequence of events in the pathogenesis of a disease is understood and accordingly treatment protocol is formulated.
Prajnaparadha (intellectual errors, or knowingly violating rules) is one of the fundamental cause of all endogenous and exogenous diseases. Asatmendriyarthasamyoga (improper union of senses with their objects) and parinama(time) are other two causative factors . These principles reveal that all idiopathic diseases of unknown etiology also have a definite cause, that needs to be searched and removed for its proper management.
In nutshell, one should initiate any treatment after acquiring complete knowledge of following:
- Inherent nature of the disease
- Its pathogenesis
- Origin or site of lesion and location of presentation
- Etiological factors. [Cha. Sa. Sutra Sthana 18/44-47]
Importance of studying Nidana section
- It is highly important to know the fundamental cause of any disease. Complete cure in curable diseases and management of palliable diseases can only be achieved after Nidana Parivarjana (removing the cause). If the cause is removed, then half the treatment is done. This stops progression of disease as well as helps the host to return to the normal state. The focus of current healthcare system is more on disease management after its complete manifestation; while Ayurveda emphasizes on identification of abnormality at an early stage, to prevent its further progression.
- The journey of a disease from the initial stage of accumulation of vitiating factors to complete manifestation of its symptoms shall be studied well for its complete knowledge.
- The knowledge of Nidana can be helpful in reducing healthcare cost by reducing use of invasive and non invasive medical diagnostic tools.
Researches
- A team of researchers compiled all Sanskrit texts of Nidana Sthana of Charak Samhita in a project report.[2]
- Shrirang S.G. have done a critical study on Nidana Sthana with special reference to Prameha Nidana [3]
- Shashirekha H. K. has studied Shosha Nidana described in Nidana Sthana. [4]
More information
The following chapters in other sections deal with detailed information about diagnostic principles and classification of disease.
- Mahachatushpada Adhyaya
- Tistraishaniya Adhyaya
- Kiyanta Shiraseeya Adhyaya
- Trishothiya Adhyaya
- Ashtodariya Adhyaya
- Maharoga Adhyaya
- Trividha Roga Vishesha Vijnaniya Vimana
- Roganika Vimana
- Vyadhita Rupiya Vimana
- Rogabhishagjitiya Vimana
Moreover each chapter of Chikitsa sthana describes the five assessment tools (nidana panchaka) of respective diseases.
All Abstracts
The new learners of Nidana sthana can read all abstracts of chapters of this section on the Abstracts- Nidana Sthana page.
References
- ↑ Available from http://spokensanskrit.org/index.php?mode=3&script=hk&tran_input=nidana&direct=au accessed on May 02,2019
- ↑ Critical Edition of Charaka Nidana Sthana available from http://ayushportal.nic.in/EMR/LITERARY_FINAL_REPORT-1.pdf downloaded on 17/04/2019
- ↑ Shrirang S.G. Thesis on Critical Study Of Caraka Nidana Sthana With Special Reference To Prameha . Department of Samhita . Institute for Post Graduate Teaching & Research in Ayurveda, Gujarat Ayurved University, Jamnagar . 2000
- ↑ Shashirekha H K . A Study On Caraka Nidana Sthana With Special Reference To Shosha . Swasthavritta . Dr. Basavaraj Nagur Memorial Rural Ayurvedic Medical College And Hospital (Dr. B N M R), Bijapur .2010