Difference between revisions of "Vata dosha"
| Line 321: | Line 321: | ||
Eighty types of diseases due to an imbalance of vatadosha(vatajananatmajavyadhi) are listed.[Cha.Sa. SutraSthana20/11][table 02]: | Eighty types of diseases due to an imbalance of vatadosha(vatajananatmajavyadhi) are listed.[Cha.Sa. SutraSthana20/11][table 02]: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | ||
| − | |+ | + | |+ Table 2: Diseases due to vata dosha |
|+ style="caption-side:bottom; | '''Table 02: 80 types of disease of vata (vatajananatmajavikara)''' | |+ style="caption-side:bottom; | '''Table 02: 80 types of disease of vata (vatajananatmajavikara)''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 12:17, 12 October 2022
Vatadoṣha is responsible for movement and cognition. [Code:SAT-B.384][1]It is one of the three sharira doṣha with a predominance of vayu and akashamahabhuta. This vital biological force performs functions like all sensory perceptions, motor activities, and higher mental activities. [Code:SAT-B.384][1]
Rigved stated that when the three dhatu- vata, pitta and kapha remain in a normal state and undisturbed, the body is at ease, and there is no disease.[R.V.1.3.6][2]Dosha, dhatu and mala are fundamental factors of the living body. [Su.Sa.SutraSthana 15/3][3][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 11/1].[4]Life continues as long as vata is present in the human body.[Bhe.Sa.SutraSthana 16/2][5]Along with being mobile, the vata may also keep the pitta, kapha, dhatu, and mala functioning. This demonstrates that vata can affect other dosha and the body's components.[Sha.Sa.Pratham Khanda 5/25][6]. Pitta, kapha, dhatu (body elements), and mala (waste materials) are dependent on vata dosha for their activities. The functions of vata are also observed in nature in the form of movements of trees, clouds, and other objects. The movement in body is a sign that life is present. Vata conducts all these gross and subtle physical movements. This article describes the details of vata dosha.
| Section/Chapter/topic | Concepts/Dosha/Vata Dosha |
|---|---|
| Authors | Bhojani M. K. 1, Tanwar Ankur Kumar 1 |
| Reviewer | Basisht G.2, |
| Editor | Deole Y.S.3 |
| Affiliations |
1 Department of Sharir Kriya, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi, India 2 Rheumatologist, Orlando, Florida, U.S.A. 3Department ofKayachikitsa, G.J.Patel Institute of Ayurvedic Studies and Research, New Vallabh Vidyanagar, Gujarat, India |
| Correspondence emails |
meera.samhita@aiia.gov.in, carakasamhita@gmail.com |
| Publisher | Charak Samhita Research, Training and Development Centre, I.T.R.A., Jamnagar, India |
| Date of publication: | , 2022 |
| DOI | In process |
Etymology and derivation
The word vata is derived from “ta” suffix to the word “Va”.The word ‘vata’ is defined as “vagatigandhanayoh”. [Su.Sa.SutraSthana 21/5][3] “Va” word is concerned with movement (gati) and intimation(gandhana). The meanings of word ‘gati’ are motion, moving, and going. The meaning of word gandhanaare intimation, information, and perception.
Synonyms[7][8]
The god of wind (maruta), movement (chala), wind(anila), present everywhere(samirana), pure (pavana), gives sensation of touch(sparshana), full of strength(mahabala), life(jivana), sadagati, help in perception of smell(gandhavaha), self-existent(swayambhu)[3][Su.Sa.NidanaSthana 1/5], air, wind, blown, desired for, wished for, solicited, and god of wind.
Various aspects
Vata is categorized as ‘dosha’primarily because of its capability to vitiate other body components. It is also mentioned as ‘dhatu’ because in normal state, it sustainsor maintainsthe body.[3] [Su.Sa.SutraSthana 21/4]It is also called as ‘mala’ as it can make the body unwholesome and produced as waste material during the process of digestion “katuavasthapaka”(last process of digestion). [Cha.Sa.ChikitsaSthana 15/11] Vata is the somatic factor having two prime functions –movements(cheshta) and process of learning or knowledge(jnana). Vata is swayambhu(self-manifested) and it is the root cause of production, preservation, and destruction.[Su.Sa.NidanaSthana 1/7][3]Vata is the controller of body. Vataleads the functions of all dosha, and its responsible for many diseases.[Su.Sa.NidanaSthana 1/8][3]
Bhautika composition
Dosha are descendants of panchamahabhuta. Vatadosha has dominance of vayu and akashamahabhuta.[9][A.S. Sutra Sthana20/2]Akasha provides space for movements, and vayuprovides the energy needed for any kind of movements. Chakrapani opines that vatadosha is originated from vayumahabhuta predominantly.[Chakrapani on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 15/8]Althoughvatadosha is panchabhautika, vatadosha is the representative of the respective mahabhuta in the human body.
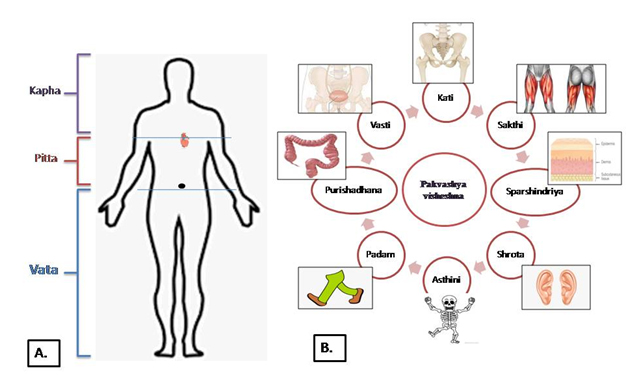
Sites of vata
Dosha pervades every part of the body. [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/9] Acharya stated the general location of vata, pitta and kapha are the lower, middle, and upper portions of the body, respectively marked by the heart(hridaya) and umbilicus(nabhi).[A.S. Sutra Sthana 1/4]Vata is predominately present in body parts below umbilicus(adhonabhi). [K.S. Sutra Sthana 27/10][10]The specific sites of dosha are locations where their functions are primarily observable. Thespecific seats of vata are:
- Urinary bladder(basti)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8] [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8]
- Large intestine+ rectum+ anal region(purishadhana)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8]
- Plevicregion(katiorshroni)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8][Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/6][3][Dalhan on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/6][3] [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4]
- Thighs(sakthini)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4]
- Both legs(padam)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8]
- All bones(asthini)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4][K.S. Sutra Sthana 27/10][10]
- Anal region(guda)[Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/6][3][Dalhan on Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/6][3][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/9][3]
- Ears(shrotra) [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4]
- Skin(sparshnendriya) [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4]
- Bone marrow(majja)[K.S. Sutra Sthana 27/10][10]
Among all these sites, large intestine(pakvashaya) is the prime site of vata.[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 12/1][4]Purishadhana included the portion of the intestine wherein purishdharakala (layer for formation and storage of stools)is located. It includesanus (guda) also. [Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/9][3][Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/6][3] Chakrapani opines that purishadhana is pakvashaya. [Chakrapani on Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/8]According to the Atharvaveda, vata is situated in the upper part of the head (mastishka). [Ath.V. 10/2/26][11]
Attributes
The characteristics of vata are:
- Dryness(ruksha)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/7][3][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/11][4]
- Coldness(shita)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/7][3] [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana 1/11][4]
- Lightness(laghu)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/7][3][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/11][4]
- Micro or subtle nature (sukshma)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/11][4]
- Mobility(chala)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/11][4]
- Clearness(vishada)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58]
- Roughness(khara)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 1/58][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/7][3][A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/11][4]
- Hardness(daruna)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 12/4]
- Bioenhancer (yogavahi)[Cha.Sa. ChikitsaSthana 3/39]
- Formlessness(amurtatva)[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 20/13]
- Frequent(bahu)[Cha.Sa. Vimana Sthana 8/98]
- Swift(sheeghra)[Cha.Sa. Vimana Sthana 8/98]
- Coarseness or harshness(parusha)[Cha.Sa. Vimana Sthana 8/98]
- Assessed through its functions(avyaktovyaktakarma)[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/7][3]
- Movements in all direction(tiryak)[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/8][3]
- Having predominately raja quality(rajobahula)[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/8][3]
- Unpredictable potential(achintyavirya)[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/8][3]
- Quick(ashukari)[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/9][3]
These attributes should be considered while taking diet and lifestyle managementof health. If the food and lifestyle habits having similar characteristics are followed in excess, a person may experience vatadoshavitiation leading to vata disorders.
Functions of vata
Vata dosha governs all bodily functions.The ability to provide other bodily entities, such as other dosha, dhatu, and mala, mobility belongs to the vatadosha in the human body.Vata is responsible for all motion, so this dosha is also known as life in living beings. [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 17/116] The principal functions of vata doshaare to sustain the body:[Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 18/49][Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/10][3][Su.Sa. ShriraSthana 7/8][3][Sh.Sa.Pratham Khand 5/21] [6]:
- Maintaining and controlling all the/ human machinery or body(tantra yantra dhara)
- The originator of all kinds of movements(parvartakachestanamucchavachanam)
- Regulates and guides the mind(niyantapranetacha manasa)
- Stimulates all sensory and motor organs(sarvendriyanamudyojakah)
- Directs senses to their respective objects(sarvendriyarthanamabhivodha)
- Responsible for proper building of the tissues and organs of the body(sarvasharira dhatu vyuhakar)
- Connects the different tissues(sandhanakarsharirasya)
- Induces speech(pravatakovacha)
- Causative factor of sound and touch sensation(prakriti sparshshabdayoshrotrasparshayormulam)
- Cause of pleasures and determination(harshautsahayonih)
- Stimulates digestive power(samirano-agneh)
- Dries up the excessive moisture(dosha samshoshanah)
- Excretion of waste products(ksheptabahimalanamor samomokshagatimata)
- Formation of every kind of channel, fine and coarse(sthulanusrotasambhetta)
- Regulates the formation of the different structures of the fetus and provides specific size/shape(kartagarbhakritinam)
- Sustain the life(ayushoanuvrittipratyayabhutah)
- Control the segmentation or division of cells(vibhagakarananmatah)[Sh.Sa.Pratham Khand 5/21] [6]
- Inhalation and exhalation(ucchavasa-nishwasa)
- Proper movements of dhatu(dhatugatisama)
Five particular functions of vata based on its types are as below:[Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 15/4][3]
- Body movements and pulsation(praspandan)
- Retain the perception of senses (udwahana)
- Ingestion of food(purana)
- Differentiation of tissues and waste products(viveka)
- Retention of waste products till evacuation(dharana)
Classification
The classification of vataisbased on different functions and locations in human body. [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana 12/8]
Five types
Prana, Udana, Samana, Vyana, and Apana are the five classifications of vatadosha. Five sets of functions by which vatadosha is divided into five types are described with [Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 15/4][3] the diseasespecificity of five types of vata.[Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/13-19][3]The location and function of five types of vatadosha based on different Ayurvedic texts are as given in table 1. [Cha.Sa. ChikitsaSthana28/5-11]
| S.No. | Type of Vata | Location | Function | Disease [Su.Sa. NidanaSthana 1/13-19][3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01. | Prana | Head (murdha) Thorax (ura) Throat (kantha) Tongue (jihwa) Mouth (asya) Nose (nasika) |
Spitting out (shthivana) Sneezing (kshavathu) Belching (udgara) Respiration (shwasa) Ingestion of food (aharadi) |
Hiccough (hikka) Asthma (shwasa) |
| 02. | Udana | Umbilicus (nabhi) Thorax (ura) Throat (kantha) |
Speech (Vakpravritti) Efforts (prayatna) Provides strength, complexion (Urjabalavarnadikarma) |
Disease occurring above the neck (Urdhvajatrugata) |
| 03. | Samana | Near digestive system (anataragneparshva) | It gives strength to the digestive system | Abdominal lump (gulma), less digestive capability (agnisada), diarrhea (atisara) |
| 04. | Vyana | Whole body (dehavyapnoti) | Movements (gati) Contraction and relaxation (prasarana) Upward and downward movements (aakeshpa) Opening and closure of eyelids (nimesha) |
disease located to the whole body (sarvadeha) |
| 05. | Apana | Scrotum (vrishana) Bladder (basti) Penis (medhra) Umbilicus (nabhi) Thorax (ura) Inguinal region (vankshana) Anus (guda) |
Ejection of semen, removal of urine and faces (Shukramutrashakritkriya), menstruation and delivery of fetus (srijtyaartavagarbha) |
Diseases related to the urinary bladder and anal region (bastigudaashraya) |
Prana
|
Udana
|
Samana
|
Vyana
|
Apana
|
Two types
Two types of dosha are: Prakrita(inherent state) and vaikritadosha (acquired state). Prakrita dosha are observed at the time of conception and are responsible for the formation of prakriti. They are constant, and any change in them leads to death or trouble. They are responsible for the expression of individuality or phenotype of the person. Vaikritadosha are produced as the waste of food (ahara) and continuously circulate in the body of fetus. They are responsible for health, and any disturbance in their physiological limits, either excess or decline, leads to disease.Prakrita and vaikritadosha always stay in connection with one another, and collectively, they are called sharirikadosha. A person can only control the vaikritadosha through diet and lifestyle. [A.S. ShariraSthana 8/4][9]
Vata dominantconstitution (prakriti)
The characteristics of vata dominantconstitution individuals based on properties of vata dosha. [Cha.Sa. Vimana Sthana 8/99]The person having vata dosha in predominance have the following characteristics:
- Leanbody appearance
- Dryness in voice, skin and hair
- Less and disturbed sleep
- Quick in action, walk, and talkative
- Unsteady movements of legs and hands
- Prominent movements of joint with voice
- Cracks in heel and skin
- Intolerance to cold
- Prominent tendons, veins and joints.
Lokapurusha samanya
Vayu is responsible for all motions in the cosmos. The vayumahabhuta is represented by the vatadosha in human body. Nourishing (visarga), depleting (adana) and distributing (vikshepa) in the universe are carried by the moon, sun and wind. Similarly, human body haskapha, pitta, and vata performing the same functions, respectively. [Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 29/6][3]
Factors responsible for abnormal states of vata
Certain factors cause excess or decline of vata in the human body. These factors are natural or unavoidable and artificial or avoidable.
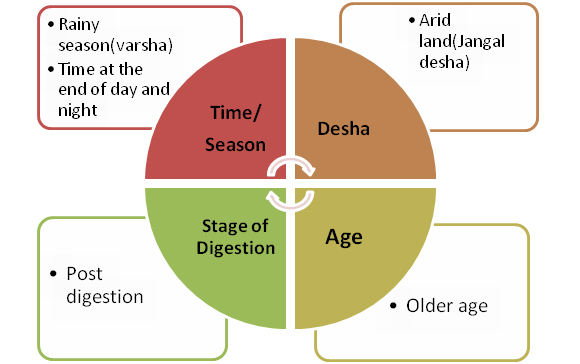
Natural factors: These factors are the essential component of biological rhythm occurring in the external as well as internal environment of the body. This natural increase is physiological. These factors are as follows:[Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana 21/20][3], [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana1/8][4], [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana12/24-25][4][A.Hr. NidanaSthana1/14-15][4]
- Season(ritu): Vata undergoes accumulation in summer(grishma), gets vitiated in rainy season(varsha) and subsides to normal during autumn(sharada).
- Various stages of digestion of food: Vata gets vitiated at the end of meal digestion(jirneanne)
- Biological rhythm of day and night: Vata gets vitiated at the end of day(apraha) and night(pratyush).
- Habitat(desha): Vata usually gets vitiated in the person of arid area(jangaladesha).
- Age (vaya): In old age, vata is in excess as compared to other dosha.
Artificial factors: Apart from natural factors, there are certain factorsthat causevitiation of dosha and disease. These factors are easily avoidable and used in clinical practice through the concept of samanyavisheshasiddhanta. These factors are as follows: [Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana21/19][3] [A.Hr. NidanaSthana1/14-15][4]
- Diet(dravya) and particular properties of diet: Ayurveda defined three tastes (rasa) that can lead to vitiation of vatadosha. These three rasa are bitter(tikta), pungent(katu) and astringent(kashaya).These three rasa, when taken in excess, cause vata vitiation(prakopa).
- Lifestyle or activities: Suppression of natural urges(vegavidharana), night awakening(ratrijagrana), loud speech(ucchabhashana), overworking or excessive shodhana(kriya atiyoga), overthinking(chinta), excessive exercise(vyayama), excessive sexual indulgence(atimaithuna), excessive studies(atiadhyanana), swimming(plavana), and lifting of weight(bharaharana) etc.
- Emaciation(karshya)
- Blackish discoloration(kashnya)
- Fond of hot articles(ushankamitva)
- Uncontrolled movements(kampa or gatrasaphurana)
- Abdominal distension(anaha)
- Constipation (shakrutgraha or gadhavarcha)
- Decreased strength(balabhransha or alpabalatvam)
- Loss of sleep(nidrabhransa or nidranasha)
- Sensory and motor function loss(indriyabhransa)
- Delirium(pralapa)
- Dizziness(bhrama)
- Lack of self-confidence(dinata)
- Dryness of skin(twakaparushya)
- Pain in bones(asthishula)
- Reduction in bone marrow(majjashosha)
- Flatulence (adhmana)
- Delusion(moha)
- Fear(bhaya)
- Grief or sorrow(shoka)
- Avoid talk (alpabhashita or alpavaka)
- Generalized weakness(angasada)
- Loss of sensation (sangyamoha or mudasangyta)
- Symptoms of increasedkapha
- Less active(mandacheshta)
- Loss of happiness or lack of pleasure (apraharsha)
- Excess salivation(praseka)
- Loss of appetite(aruchi)
- Nausea(rhallasa)
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 National AYUSH Morbidity and Standardized Terminologies Electronic Portal by Ministry of AYUSH Available on http://namstp.ayush.gov.in/#/Ayurveda
- ↑ Rg-vedasamhita. Hindi translation by Pt. Ram Govind Trivedi.Varanasi: ChowkhambaVidyabhawan; 2016.
- ↑ 3.00 3.01 3.02 3.03 3.04 3.05 3.06 3.07 3.08 3.09 3.10 3.11 3.12 3.13 3.14 3.15 3.16 3.17 3.18 3.19 3.20 3.21 3.22 3.23 3.24 3.25 3.26 3.27 3.28 3.29 3.30 3.31 3.32 Sushruta. Sushruta Samhita. Edited by JadavajiTrikamjiAacharya. 8th ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Orientalia;2005.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 Vagbhata. Ashtanga Hridayam. Edited by HarishastriParadkar Vaidya. 1st ed. Varanasi: Krishnadas Academy; 2000
- ↑ Bhel. Bhel Samhita. Edited by Priya Vrat Sharma. Reprint ed. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Visvabharti;2008.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Sharngdhara. Sarngadhara Samhita. Edited by Parashuram Shastri Vidyasagar.. Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharatiPrakashan ;2013.
- ↑ Shabdakalpadruma, Radhakantdev R, editors. Volume 3, Delhi: Amar Publication; 2018, Available on Mana.
- ↑ Monier-Williams, Monier William's Sanskrit-English Dictionary, 2nd Ed., Oxford University Press;1899.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 Vagbhata. Ashtanga Samgraha. Edited by Shivprasadsharma. 3rd Ed., Varanasi: Chowkhamba Sanskrit Series Office; 2012.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Kashyapa. Kashyapa Samhita. Edited by P. V. Tewari. Reprint. Varanasi: Chaukhambha vishvabharati;2008.
- ↑ Atharvaveda Samhita. Edited by Shriram Sharma Acharya. Mathura: YugNirman Yojana: 2005.
Clinical aspects
Preventive aspect: Person having prakriti vatadosha as body constitution should avoid diet and lifestyle which vitiates vata dosha.To prevent the vata dominant diseases, diet and lifestyle opposite to attributes of vata are advised.[A.Hr. ShariraSthana3/85-89][4]
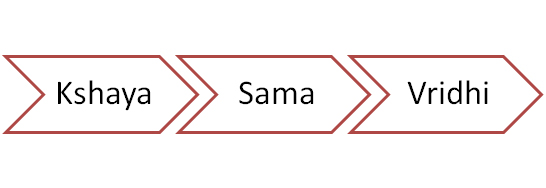
Stages of dosha: Dosha continues to exist in three states: hypofunction (kshaya), hyperfunction (vriddhi), and normal physiological state (sama). [Cha.Sa. Sutra Sthana17/110]Increase and reduction in dosha functioning (karma), respectively, can be used to understand dosha increase and decline in the body.Dosha, when increased, produce their respective features in excess; when decreased, cut off their functions and when in normal state, they perform their normal functions.
Hyperfunctioning of vata(vridhilakshana): When vata levels in the body are increasing, the body exhibits various signs and symptoms as below: [Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana15/15][3], [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana11/5][4], [A.S. Sutra Sthana 19/6][9]:
Hypo functioning of vata (kshayalakshana): When vata levels in the body are declining, the body exhibits various signs and symptoms as below:[Su.Sa. Sutra Sthana15/9][3] , [A.Hr. Sutra Sthana11/15-16][4], [A.S. Sutra Sthana19/15][9]
Diagnosis
The state of vata dosha can be diagnosed and assessed based on clinical features. The most presented clinical features of vata dosha are pain(shula), numbness(suptata), dryness(rukshta) rigidity(stambhana), wasting (shosha)and harshness(parusha).[Cha.Sa. SutraSthana20/12] Eighty types of diseases due to an imbalance of vatadosha(vatajananatmajavyadhi) are listed.[Cha.Sa. SutraSthana20/11][table 02]:
| Cracks in nail(nakhabheda) | Diarrhea(vidbheda) | Difficulty in vision(akshibheda) | Frontal pain(lalatabheda) |
| Cracks in feet(vipadika) | Dysperistalsis(udarvarta) | Toothache(dantabheda) | Headache(shiroruka) |
| Foot pain(padashula) | Unable to walk (khanjata) | Loose teeth(dantashaithilya) | Scaling in scalp(keshabhumisphutana) |
| Foot drop(pada bhransha) | Kyphosis(kubjata) | Aphasia(mukatva) | Facial paralysis(ardita) |
| Foot numbness(pada suptata) | Dwarfism(vamanatva) | Speech disorder(vakasanga) | Monoplegia(ekangaroga) |
| Difficulty in walking (vatakhuddata) | Stiffness of sacroiliac joint(trikagraha) | Astringent taste in mouth(kashayasyata) | Quadriplegia (sarvangaroga) |
| Stiffness in ankle(gulphagraha) | Back stiffness(prishtagraha) | Dry mouth(mukhashosha) | Hemiplegia(pakshavadha) |
| Cramps in calf(pindikodveshtana) | Lateral side Chest pain(parshvavamarda) | Tastelessness (arasagyata) | Clonic contraction(akshepaka) |
| Sciatica(gridhrasi) | Pain abdomen(udaraveshta) | Anosmia(grananasha) | Tonic contraction(dandaka) |
| Genu varum(janubheda) | Stiffness in heart(hridmoha) | Earache(karnashula) | Fainting(tama) |
| Genu valgum(januvishlesha) | Heaviness in heart(hriddrava) | Tinnitus (ashabdashravana) | Giddiness(bhrama) |
| Stiffness in thigh(urustambha) | Rubbing pain in chest(vakshauddharsa) | Difficult hearing(ucchaihsruti) | Tremors(vepathu) |
| Thigh pain(urusada) | Difficulty in thoracic cage muscle movements(vakshauparodha) | Deafness (badhirya) | Yawning(jrimbha) |
| Paraplegia(pangulya) | Stabbing pain in chest(vakshastoda) | Ptosis of eye lid(vartmastambha) | Hiccups (hikka) |
| Rectum prolapse(gudabhransha) | Wasting of arm muscles(bahushosha) | Entropion (vartmasankocha) | Depression(vishada) |
| Tenasmus (gudarti) | Neck stiffness(grivastambha) | Glaucoma (timira) | Delirium(atipralapa) |
| Scrotum pain(vrushnakshepa) | Torticollis(manyastambha) | Pain in eye(akshishula) | Dryness(rukshya) |
| Stiffness in penis(shephastambha) | Hoarseness of voice (kanthoddhvansa) | Complete Loss of vision(akshivyudasa) | Hardness(parushya) |
| Tension in groin area(vankshanaanaha) | Difficult movement of tempo-mandibular joint(hanubheda) | complete loss of eye brow(bhruvyudasa) | Dusky appearance (shyavarunaavbhasata) |
| Pelvic girdle pain(shronibheda) | Cracks in lips(oshthabheda) | Temporal pain(sankhabheda) | Insomnia(aswapana) |
Send us your suggestions and feedback on this page.